Warning! This series of SEO guides will be exhaustive. No bullsh*t! I’ll explain everything step-by-step and in detail.
So, you’ve been warned.
What Is SEO?
SEO – Search Engine Optimization is the activities or processes to help the search bots see and recognize the content we see visually on the site and to bring the site to the forefront in the SERP – Search Engine Results Pages.
For instance, when we look at Miro‘s homepage design visually, it looks beautiful with its colorful textured background; however, that’s not what the search engines see.
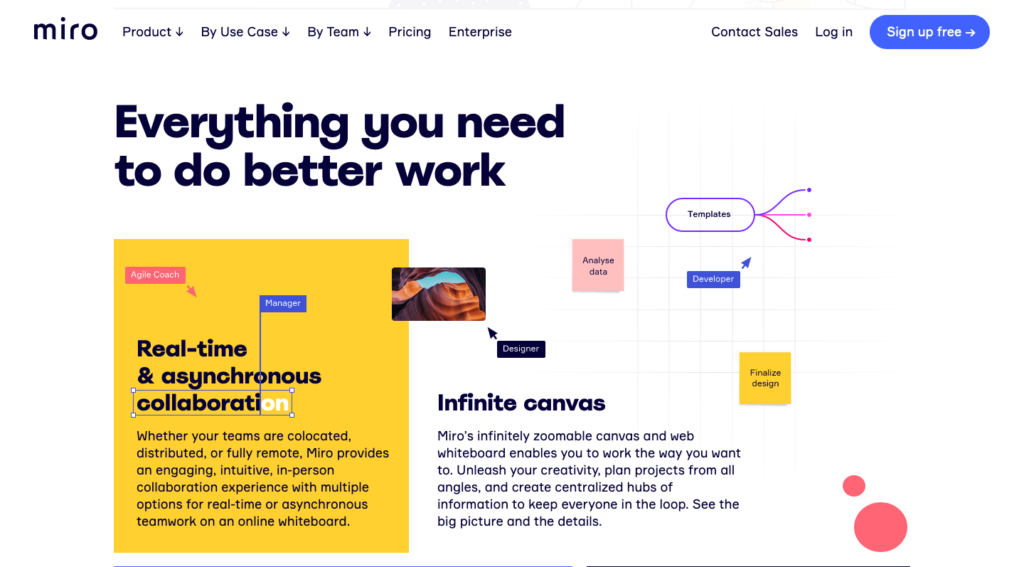
Instead, they see this:
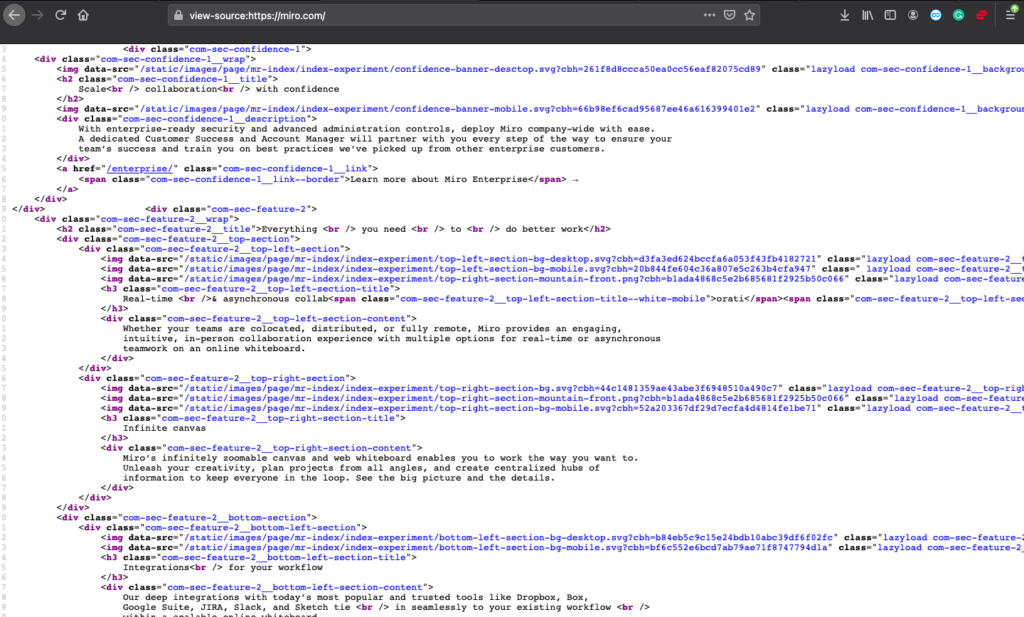
So, regardless of the hard work you’ve put to the site-front, the search bots see nothing other than a bunch of codes in their own way of understanding. Thus, if you want your site to be SEO-friendly, you need to explain your site and content in the language they understand.
Another example. You see that the title of this page is bigger than the paragraph while the search bots see is:
<h1 class=”entry-title text-center”> SEO Basics: Exhausting Introduction To SEO For Beginners </h1>
One more example. The <strong> and <bold> tags both make a text seem bold but search engines perceive the <bold> and <strong> tags as different since the <strong> tag indicates the importance of a copy and <bold> tag changes only how the word seems.
Question may arise: Can we achieve better results by adding <strong> instead of <bold> to the keywords we want to rank for?
The answer would be that, better not to play too hard since it can be understood as over-optimization and spam.
From <h1> to <h6> tags are the HTML header tags which stand for the importance of the headers in a HTML page. On this page, <h1> tag in the title means the most important heading on this page is the title.
PS: the page title, post title, and SEO title are totally different things:
- “The
<title>element defines the title of the document. The title must be text-only, and it is shown in the browser’s title bar or in the page’s tab.
The <title> element:
– defines a title in the browser toolbar
– provides a title for the page when it is added to favorites
– displays a title for the page in search engine results.” – W3Schools
- The SEO title or meta tag is shown to users in the SERP. It will be the title of your snippet in the search engines. SEO title can be different than the post title – H1 heading on the page to be appealing for users to click on it.
PSS: it’s strongly advised to use <h1> only once per page since you cannot say google that on my page there’re two “THE most important headers.” If you want to increase the size, just use the style attribution:
<h1 style=”font-size:45px;”> Post title </h1>
Keep in mind that headings should be used in ascending or descending order i.e.,
…
<h2> Text </h2>
<h3> Text </h3>
<h3> Text </h3>
<h2> Text </h2>
…
Not,
…
<h1> Text </h1>
<h3> Text </h3>
<h5> Text </h5>
<h2> Text </h2>
…
So, be sure that you check the HTML structure of your web pages. Personally, I use the following tools to check the structure:
- “SEO META in 1 CLICK” is a Chrome extension that summarizes and displays all metadata like script tags, links, headers, and other relevant information to work on SEO efficiently.
- Browseo.net mostly focuses on pure HTML; the way search engines see when they visit a page. This website shows headers, content length, number of external and internal links, META information such as meta tag, title, and more.
- With view-source:https://site.com – you can check the HTML source of a web page.
- You can also check the summary of CSS and HTML by inspecting a page or specific element by selecting a text and clicking the right button of the mouse.
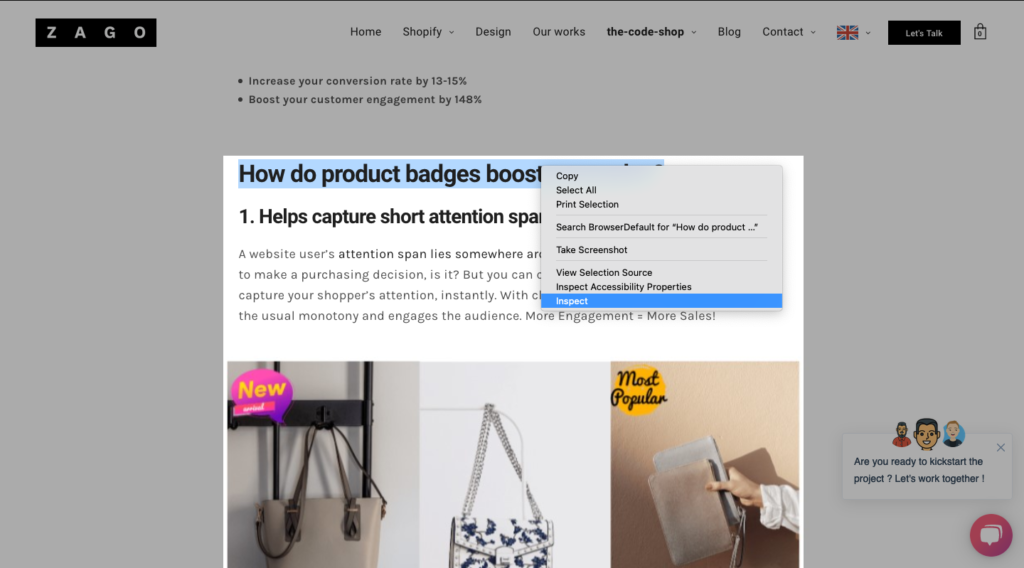
By inspecting, for instance, a certain heading, you’ll see how the element details. For this inspected heading, you can see that it’s bold and written in <h2> tag:
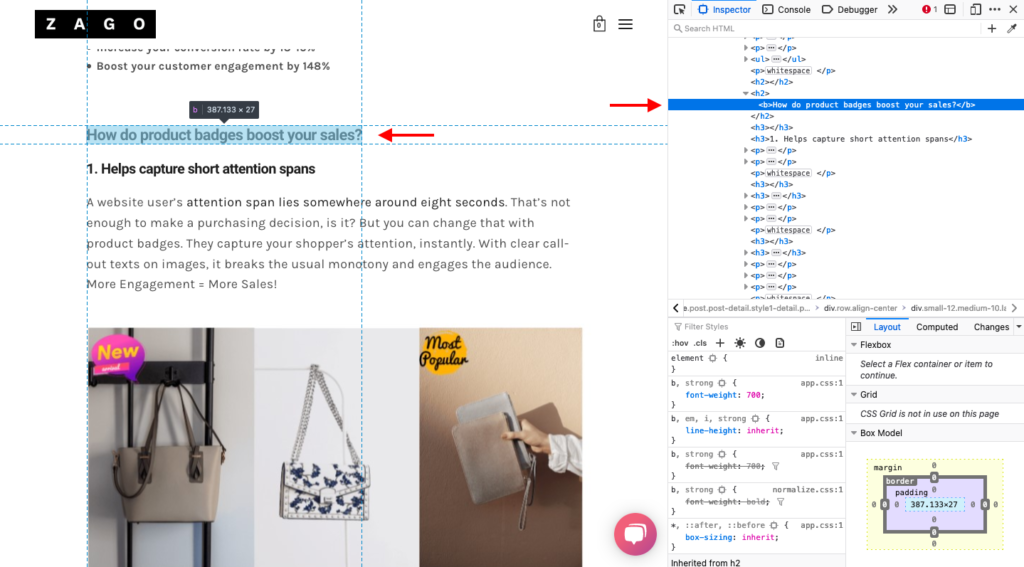
Types of SEO
How many types of SEO out there? Let’s say 3 to 6 depending on the interpretation.
The main types of SEO are:
- Technical SEO
- On-page SEO
- Off-page SEO
Technical SEO is the process of making sure that websites are crawling and indexed properly by search engines. It includes a lot of technical details such as XML sitemap generation, Structured Data, etc., which I’ve elaborated more in my other blog called
On-page SEO practices include proper use of headings and keywords, URL structure for pages, optimization of images by using alt tags.
Off-page practices consist mostly of outbound link building strategies combined with Social Media Marketing, forums, networking sites, and other activities that are done outside a site.
The other types of SEO can be categorized of the transparency of the optimization process:
- White Hat SEO
- Black Hat SEO
- Grey Hat SEO
White Hat SEO is the “rightful” practice accepted by search engines. This includes optimization of content, keyword research and getting backlinks in natural ways.
Black Hat SEO, also called negative SEO, are the practice of optimization techniques that are the manipulation of indexing through sneaky ways such as keyword stuffing, cloaking, and other activities which are eventually punished by the search engines if they catch it (creepy winking).
Grey Hat SEO is riskier than White Hat SEO, and the practices include clickbait content, paid (not sponsored) links and reviews, getting backlinks from the same domain with guest blogging, etc. that may or may not be punished.
How Google works? 3 stages of serving search results
Google receives over 63,000 searches per second; it is 5.6 billion searches a day. And, it uses over 200 factors in its algorithm before delivering the best SERP results. That’s pretty much.
As you might already know, Google’s automated programs are “in charge” to find the best relevant web pages and serve search results. How? How Google works?
PS: Because Google has 2.5 trillion searches per year, I mention Google mostly.
In this post, we’ll look closer to the three stages of Google search:
- Crawling
- Indexing
- Serving search results – ranking
Let’s begin.
Crawling
Google uses search engine software that’s known as “web crawlers.” Web crawlers, or spiders are looking for new or updated pages. The spiders then store these pages in their web index to use later. They find these new or updated pages in different ways, such as following links mentioned in the pages. Many other factors affect Google spiders’ fetching your web pages. For now, let’s keep this topic for the next article.
Indexing
Simply, the indexing process is about Google understanding what the crawled pages are about. While preparing your content and practicing SEO, ask yourself questions like:
- How do you distribute your brand keywords throughout the website and pages?
- Do your contents include the main keywords and synonyms?
- Do your URLs contain keywords?
- Do you use visual content? Etc.
Serving search results – ranking
In 2020, Google had a new update that I found so efficient. As you may have noticed, when you click a result on a featured snippet in a SERP result, on the page, you are automatically heading to the exact text, highlighted by yellow. Google takes users to the precise text on an HTML page with SCROLL to the text technique.
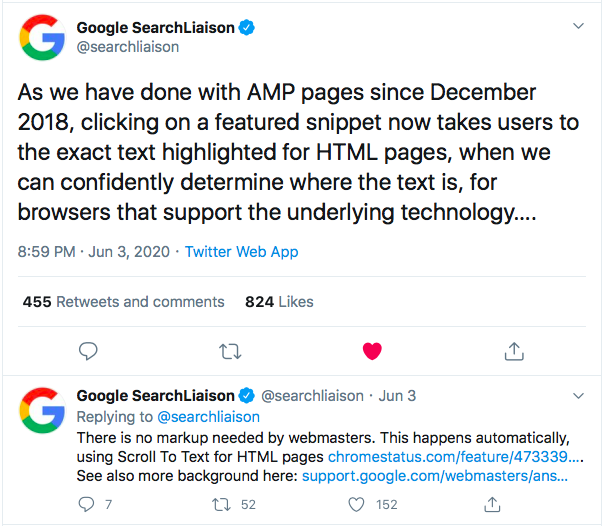
As you see, Google search quality engineers are continually improving search results to serve users the best. For this, you are also somehow in charge if you want people to reach your content; you need to consider over 200 factors that affect ranking to optimize your website perfectly. Just keep in mind that SEO is not a one-time practice; you need to work on search engine optimization regularly.
Fetching spiders
So, Google’s software programs called spiders fetch web pages and store them in Google’s index of the web. This fetching process continues with finding other pages by following the pointed links. At the end of the fetching, if there is an end, Google stores billions of web pages to use and retrieve search results later.
Here I put an article you’d want to check out which discusses the importance of internal linking practices for SEO.
Matt Cutts, the former Google engineer, explained what happens when a user searches on Google. He says that when Internet users start searching on Google, they don’t search on Google, but Google’s index of the web. Then Google software starts searching the index and finds millions of results that can show users.
How Google is going to show the users, the SERP depends on your website’s content and other 200+ ranking factors. In short, those factors are:
- Content relevancy
- Keyword and its synonyms: usage and density
- Domain authority
- Page load speed
- PageRank, etc.
That is just the beginning. Ranking higher on the SERP is hard yet possible. It requires a considerable time investment but gives fantastic results with patience and the right strategy.